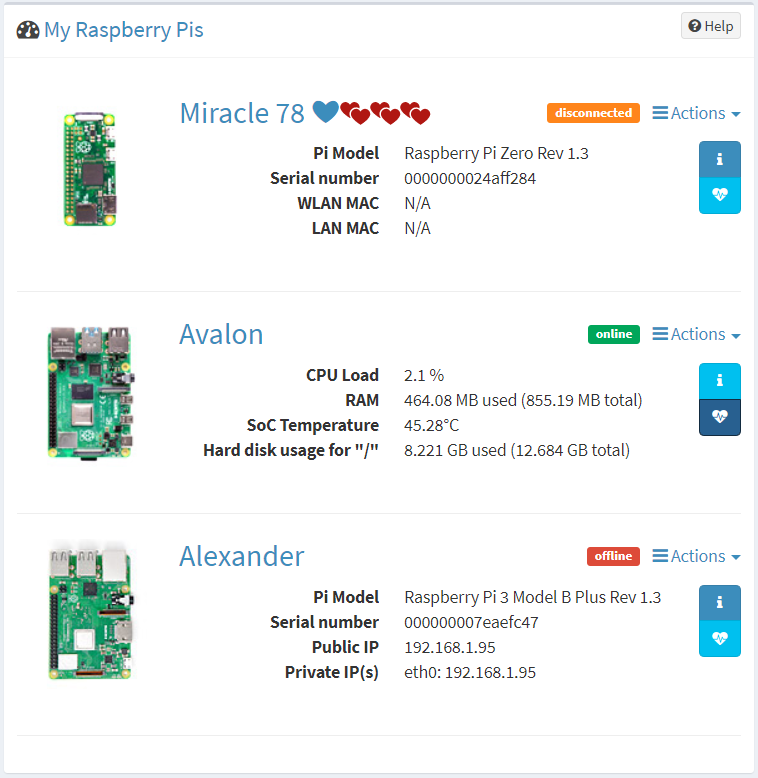
Ever wondered how you can keep tabs on your Raspberry Pi's health without breaking a sweat? Monitoring your Raspberry Pi’s performance is crucial whether you're running it as a media center, home server, or even a weather station. In this guide, we’ll explore everything you need to know about how to monitor your Raspberry Pi health like a pro.
Picture this: you’ve spent hours setting up your Raspberry Pi for a project, only to find out later that it’s been overheating or running out of storage. Not cool, right? That’s why understanding how to monitor your Raspberry Pi health is a game-changer. It’s like giving your Pi a regular check-up to make sure it’s running smoothly.
Don’t worry if you’re new to this. We’ve got you covered with step-by-step instructions, tips, and tricks to ensure your Raspberry Pi stays in tip-top shape. By the end of this article, you’ll have all the tools you need to keep your Pi running like a champ.
Read also:Jack Blacks Home Where Does The Legendary Actor Live
Here’s a quick rundown of what we’ll cover:
- Why Monitoring Raspberry Pi Health Matters
- Tools and Methods for Raspberry Pi Monitoring
- Setting Up Alerts for Critical Issues
- Best Practices for Maintaining Your Pi
Ready to dive in? Let’s get started!
Why Is Monitoring Raspberry Pi Health Important?
Monitoring your Raspberry Pi health isn’t just about keeping it running—it’s about ensuring it runs efficiently and reliably. Think of your Pi as a small powerhouse that needs care and attention. If you neglect it, you might face issues like overheating, disk errors, or even hardware failure.
By monitoring your Raspberry Pi, you can:
- Prevent hardware damage by detecting overheating early.
- Optimize performance by identifying resource bottlenecks.
- Ensure data integrity by monitoring disk usage and errors.
It’s like having a personal mechanic for your Pi. You wouldn’t drive a car without checking the oil, right? Similarly, you shouldn’t run a Raspberry Pi without monitoring its health.
Tools You Can Use to Monitor Raspberry Pi Health
Now that you know why monitoring is important, let’s talk about the tools you can use. There are plenty of options out there, from simple command-line utilities to advanced monitoring dashboards. Here’s a breakdown of some of the best tools:
Read also:Ayushi Jaiswal The Rising Star Of Indian Cinema
1. htop: The Ultimate Command-Line Task Manager
htop is a powerful tool for monitoring CPU, memory, and disk usage in real-time. It’s like Task Manager on Windows but way cooler. You can install it by running:
sudo apt install htop
Once installed, simply type htop in the terminal to see a detailed overview of your Pi’s performance.
2. vcgencmd: Check Temperature and Voltage
vcgencmd is a built-in command that lets you check your Pi’s temperature, voltage, and clock speed. Here’s how you can use it:
vcgencmd measure_temp– Check the current temperature.vcgencmd measure_volts– Check the voltage levels.
These commands are super handy for diagnosing overheating or power supply issues.
3. Glances: A Cross-Platform Monitoring Tool
Glances is another fantastic tool that provides a comprehensive overview of your Pi’s health. It supports multiple platforms and can even generate web-based dashboards. To install:
sudo apt install glances
Run glances in the terminal to see a beautiful dashboard with all the stats you need.
Setting Up Alerts for Critical Issues
What good is monitoring if you don’t get notified when something goes wrong? Setting up alerts is crucial for maintaining your Raspberry Pi’s health. Here’s how you can do it:
1. Using crontab for Scheduled Checks
cron is a scheduling tool that lets you run commands at specific intervals. You can use it to check your Pi’s temperature and send an email if it exceeds a certain threshold. Here’s an example:
*/5 * * * * vcgencmd measure_temp | grep -q "temp=80.0" && echo "Your Pi is overheating!" | mail -s "Pi Alert" your_email@example.com
This command checks the temperature every 5 minutes and sends an email if it hits 80°C.
2. Pushbullet for Instant Notifications
Pushbullet is a great app for sending notifications to your phone or computer. You can integrate it with your Pi to get real-time alerts. Here’s how:
- Install the Pushbullet CLI tool on your Pi.
- Set up a script to send notifications when certain conditions are met.
It’s like having a personal assistant that keeps you informed about your Pi’s status.
Understanding Raspberry Pi Temperature
Temperature is one of the most critical factors affecting your Pi’s health. Overheating can lead to throttling, crashes, or even permanent damage. Here’s how you can manage it:
1. Use a Heat Sink or Fan
Investing in a good heat sink or fan can make a world of difference. They help dissipate heat and keep your Pi cool under load. Some fans even come with temperature sensors to adjust their speed automatically.
2. Monitor Temperature Regularly
As we discussed earlier, vcgencmd is your go-to tool for checking temperature. Make it a habit to monitor it regularly, especially if your Pi is running intensive tasks.
Managing Disk Space on Raspberry Pi
Running out of disk space is a common issue, especially if you’re using a small SD card. Here’s how you can manage it:
1. Use df to Check Disk Usage
df -h is a simple command that shows you how much space is available on your SD card. It’s a quick way to identify if you’re running low.
2. Clean Up Unnecessary Files
Regularly clean up old files, logs, and cache to free up space. Tools like bleachbit can help automate this process.
Best Practices for Maintaining Your Raspberry Pi
Here are some best practices to keep your Raspberry Pi healthy:
- Regularly update your software using
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade. - Backup your SD card regularly to prevent data loss.
- Use a stable power supply to avoid voltage issues.
Following these practices will ensure your Pi stays in top condition.
Troubleshooting Common Raspberry Pi Issues
Even with monitoring, issues can still arise. Here’s how to troubleshoot them:
1. Overheating
If your Pi is overheating, check the following:
- Is the cooling system working properly?
- Are there any obstructions blocking airflow?
2. Slow Performance
Slow performance could be due to:
- High CPU or memory usage.
- Insufficient storage space.
Use tools like htop or glances to identify the root cause.
Conclusion: Keep Your Raspberry Pi Healthy and Happy
Monitoring your Raspberry Pi health doesn’t have to be complicated. With the right tools and practices, you can ensure your Pi runs smoothly for years to come. Remember to:
- Regularly check temperature, disk usage, and performance metrics.
- Set up alerts for critical issues.
- Follow best practices for maintenance.
So, what are you waiting for? Start monitoring your Raspberry Pi today and take your projects to the next level. Don’t forget to share your thoughts in the comments below or check out our other guides for more tips and tricks. Happy hacking!